What is Tubal Ligation?
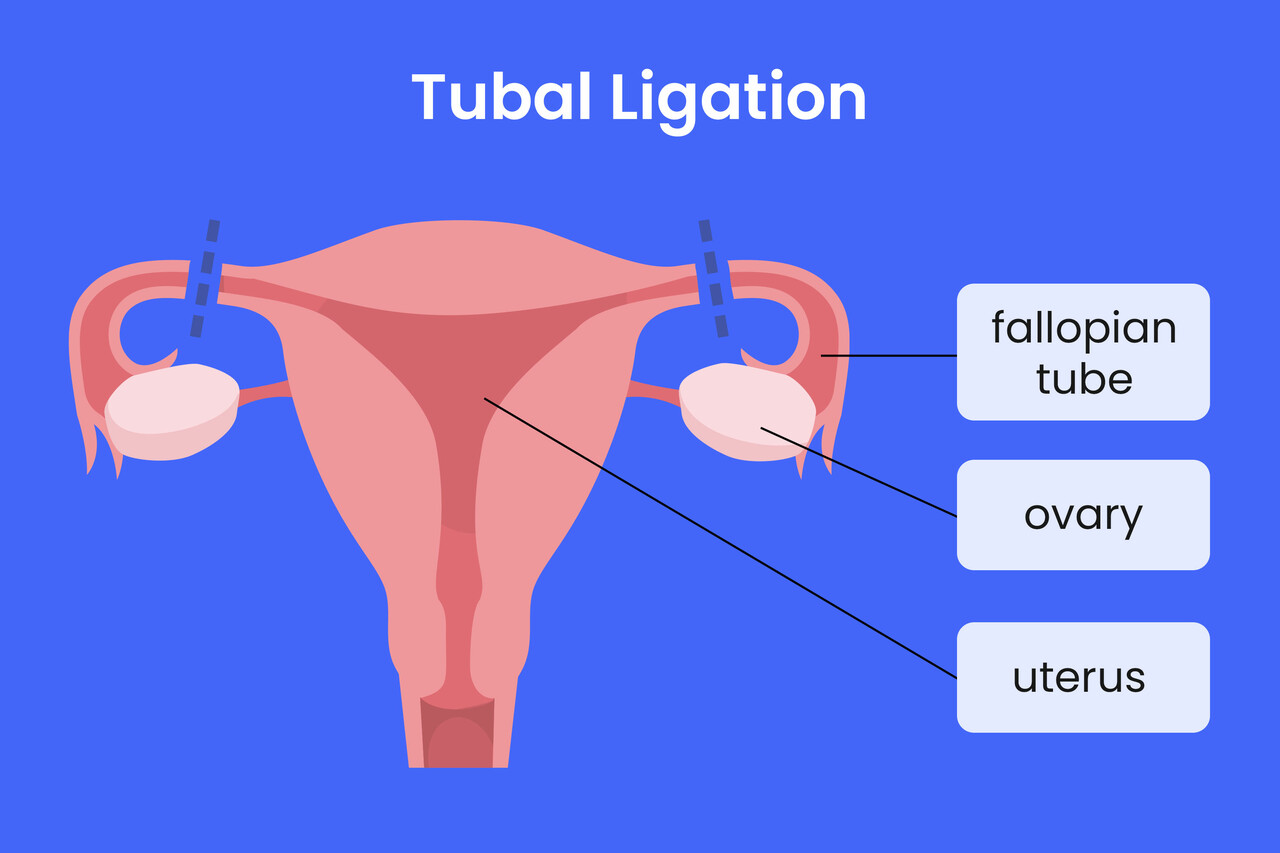
Tubal ligation, commonly known as “getting your tubes tied,” is a permanent method of female sterilization. In this procedure, a woman’s fallopian tubes are cut, tied, or sealed to prevent eggs from reaching the uterus for fertilization, thus preventing pregnancy. It is a widely chosen contraceptive option for women who are certain they do not want more children.
We use advanced diagnostic tools and safe, effective treatments to ensure optimal vaginal health at every stage of a woman’s life. Whether you seek preventive care, medical management, or surgical solutions, trust us for your complete vaginal health needs.
Symptoms or Indications for Tubal Ligation
Tubal ligation is an elective procedure with no “symptoms” as it is not a disease treatment. However, it is indicated for:
- Women who desire permanent birth control
- Women for whom pregnancy poses health risks
- Those who do not wish to use temporary contraceptive methods
- Women undergoing cesarean section (can be done simultaneously if planned)
Procedure / Treatment
Tubal ligation can be performed through:
- Laparoscopy (Minimally Invasive Surgery)
A small incision is made near the navel, and a laparoscope is inserted to view the tubes. The tubes are then cut, tied, or sealed using clips, rings, or electric current (electrocautery). - Mini-laparotomy (Postpartum Tubal Ligation)
Performed soon after childbirth through a small abdominal incision below the navel. - During Cesarean Section
Tubes are tied immediately after the baby is delivered through the same abdominal incision.
The procedure is usually done under general or regional anesthesia and takes about 30 minutes. Most women go home the same day or after a short hospital stay.
Prevention (Alternative to Tubal Ligation)
Since tubal ligation is a preventive measure for pregnancy, alternatives include:
- Oral contraceptive pills
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
- Contraceptive injections or implants
- Barrier methods like condoms or diaphragms
These methods are reversible, unlike tubal ligation, which is considered permanent.
Benefits of Tubal Ligation
- Permanent Birth Control: No need for daily or monthly contraceptive measures.
- Highly Effective: Over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy.
- No Hormonal Side Effects: Unlike hormonal birth control, it does not affect natural hormonal balance.
- Cost-Effective: One-time procedure eliminates long-term contraceptive costs.
- Quick Recovery: Especially when done laparoscopically.
Types of Tubal Ligation
- Tubal Clips or Rings: Applying clips or bands to block the tubes.
- Electrocautery (Burning/Sealing): Using electric current to seal sections of the tubes.
- Tubal Cutting and Tying: Removing a small part of the tube and tying the ends (most common).
- Fimbriectomy: Removal of the end portion of the tube near the ovary (less common).
- Salpingectomy: Complete removal of the fallopian tubes, often done for cancer risk reduction along with sterilization.
