What is Rectal Prolapse?
Symptoms of Rectal Prolapse
- A visible bulge or protrusion from the anus, especially during or after a bowel movement
- Sensation of incomplete bowel emptying
- Mucus or blood discharge from the rectum
- Fecal incontinence or difficulty controlling bowel movements
- Rectal pain or discomfort
- Constipation or frequent urge to defecate
- Feeling of fullness in the rectal area
If left untreated, rectal prolapse can worsen over time and lead to complications like infection, tissue damage, or obstruction.
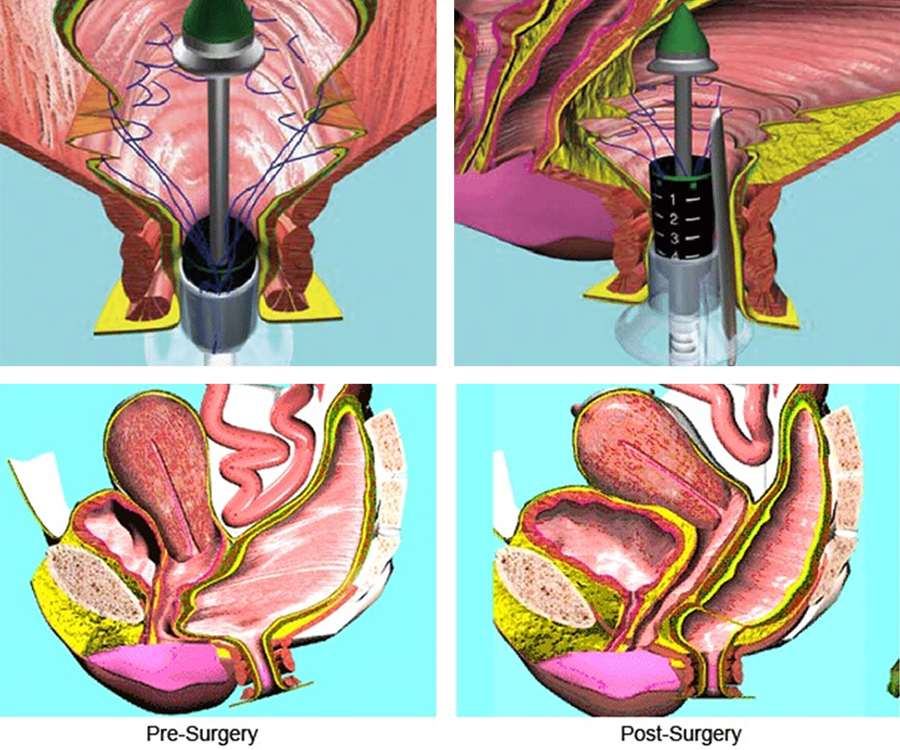
Surgical Treatment for Rectal Prolapse
Surgery is the most effective and long-term treatment for rectal prolapse. It aims to repair and reposition the rectum, restore bowel function, and relieve symptoms. The type of surgery depends on the patient’s age, overall health, severity of prolapse, and presence of other medical conditions.
Common Surgical Procedures Include:
Abdominal Rectopexy (Laparoscopic or Open):
The rectum is lifted and secured to the sacrum (a bone in the pelvis) using sutures or mesh.
Often performed laparoscopically (minimally invasive), which results in quicker recovery.
Perineal Procedures (Perineal Rectosigmoidectomy or Delorme Procedure):
Done through the anus, suitable for elderly or high-risk patients.
Involves removing the prolapsed segment and reattaching the healthy portion.
Robotic-Assisted Rectopexy:
A modern, minimally invasive technique offering greater precision and shorter recovery time.
Prevention Tips
While not always preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk of rectal prolapse:
- Eat a fiber-rich diet to prevent constipation
- Stay hydrated
- Avoid straining during bowel movements
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Practice pelvic floor strengthening exercises (like Kegels)
- Seek timely treatment for chronic cough, constipation, or diarrhea
Benefits of Surgery for Rectal Prolapse
- Permanent correction of the prolapse
- Improved control over bowel movements
- Relief from discomfort, pain, and bleeding
- Enhanced quality of life and confidence
- Reduced risk of recurrence or complications
Types of Rectal Prolapse
Full-thickness (Complete) Prolapse:
The entire wall of the rectum protrudes through the anus.
Mucosal Prolapse:
Only the inner lining of the rectum slides out.
Internal (Occult) Prolapse or Intussusception:
The rectum folds into itself without coming out through the anus, often causing constipation and discomfort.
