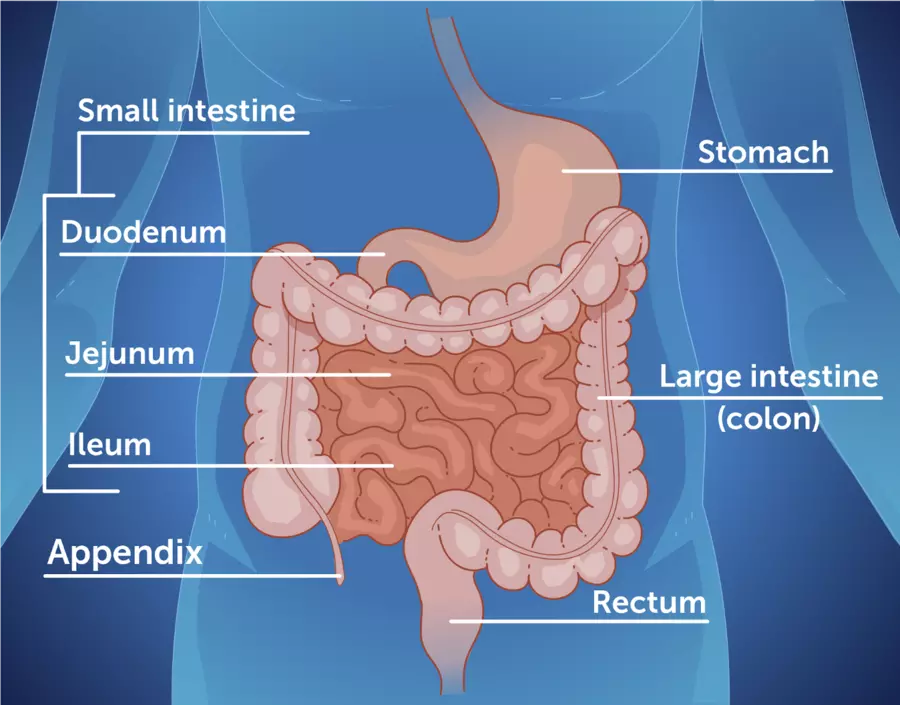
What is Small Bowel Resection?
Symptoms That May Indicate the Need for Small Bowel Resection
The symptoms depend on the underlying condition, but common indicators include:
- Severe abdominal pain or cramping
- Bloating or distension
- Nausea and vomiting
- Inability to pass gas or stool (bowel obstruction)
- Blood in stool
- Chronic diarrhea (especially in Crohn’s disease)
- Weight loss or malnutrition
- Fever and signs of infection (with perforation)
Procedure or Treatment Overview
Preoperative Preparation:
- Diagnostic tests such as CT scans, X-rays, endoscopy, or MRI
- Fasting and bowel preparation
- Evaluation of overall health and fitness for surgery
Surgical Procedure:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered.
- Incision: Surgery may be done using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopy.
- Removal: The diseased or damaged portion of the small intestine is removed.
- Reconnection: The healthy ends of the intestine are stitched together (anastomosis).
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures or staples.
If reconnection is not possible immediately, a stoma (ileostomy) may be created to allow waste to exit the body through the abdominal wall.
Recovery:
- Hospital stay of 3–7 days (depending on condition and technique used)
- Gradual return to normal diet
- Pain management and wound care
- Follow-up visits to monitor healing and bowel function
Prevention (Where Possible)
While not all causes of small bowel resection can be prevented, certain steps can reduce the risk:
Timely treatment of Crohn’s disease to prevent complications
Regular screening for polyps or tumors
Avoiding ingestion of foreign bodies or harmful substances
Managing abdominal injuries and infections promptly
Following a doctor-advised anti-inflammatory or low-residue diet (for Crohn’s patients)
Benefits of Small Bowel Resection
Relief from painful and life-threatening symptoms
Restoration of normal bowel function
Prevention of further damage or complications
Improved nutritional absorption (in certain cases)
Increased quality of life, especially for Crohn’s patients
Types of Small Bowel Resection
Partial Resection: Only the affected portion of the small intestine is removed.
Total Small Bowel Resection: Extremely rare, involves removal of most or all of the small intestine.
Segmental Resection: Removal of a specific segment such as the ileum or jejunum.
Laparoscopic Resection: Minimally invasive approach with quicker recovery.
Open Resection: Traditional method used for severe or complex conditions.
Ileostomy Creation: Temporary or permanent stoma may be formed if bowel reconnection isn’t possible immediately.
Common Conditions Treated with Small Bowel Resection
Intestinal Obstruction (due to adhesions, hernias, or tumors)
Crohn’s Disease (when unresponsive to medical therapy)
Intestinal Perforation
Bleeding Ulcers or Polyps
Cancer of the Small Intestine
Ischemia or Necrosis (tissue death due to poor blood flow)
