What is Laparoscopic Tubal Ligation?
Symptoms or Reasons for Considering Tubal Ligation
Laparoscopic tubal ligation is not done to treat symptoms but is chosen by women who:
- Do not wish to have children in the future
- Have completed their family
- Want a permanent birth control solution
- May have health conditions where pregnancy poses a risk
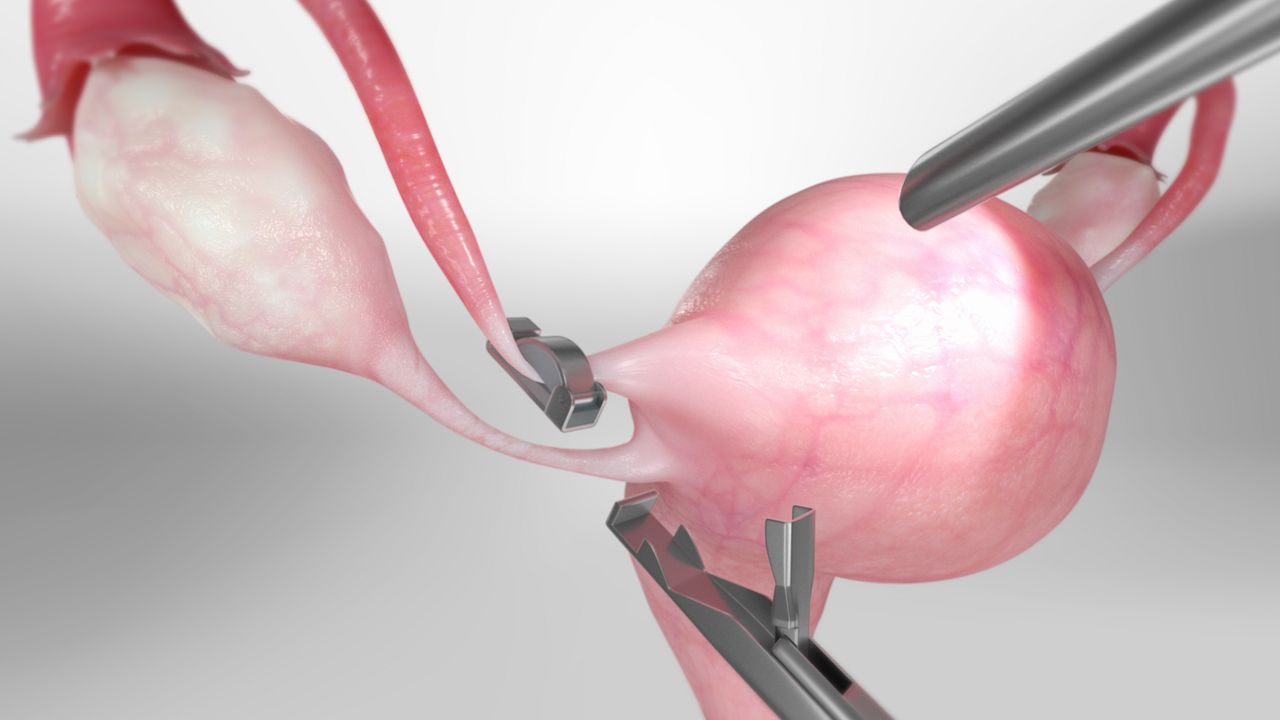
Procedure or Treatment
Preparation: You will be asked to fast for a few hours before the surgery. Anesthesia and preoperative assessments are done.
Surgery:
Performed under general anesthesia.
A small incision is made near the navel.
A laparoscope (thin tube with camera) is inserted to view the fallopian tubes.
Additional small incisions may be made to insert surgical instruments.
The tubes are sealed by clipping, cutting, or cauterizing (burning).
Completion: The instruments are removed, and the small incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape.
Duration: The procedure usually takes 20-30 minutes.
Recovery: Most women return home the same day and resume normal activities within a few days, with full recovery in about a week.
Prevention
Benefits of Laparoscopic Tubal Ligation
- Permanent contraception: Eliminates the need for daily pills or temporary methods.
- Highly effective: Over 99% success rate in preventing pregnancy.
- Minimally invasive: Smaller incisions, less pain, and quicker recovery compared to open surgery.
- Same-day discharge: Most procedures are done as day care surgeries.
- No effect on hormones: Does not interfere with menstrual cycle or hormonal balance.
- Cost-effective in long term: Avoids repeated costs of temporary contraceptives.
Types of Tubal Ligation Methods
Laparoscopic Tubal Ligation
Clips or rings (Filshie clip, Falope ring)
Electrocoagulation (burning part of the tube)
Partial tubal removal
Mini-laparotomy Tubal Ligation
Often done after childbirth (postpartum sterilization) through a small abdominal incision.
Hysteroscopic Sterilization (Essure – now discontinued in many countries)
A non-surgical method that involved placing inserts into the tubes.
