What is Gastrojejunostomy?
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Surgery
Patients suffering from conditions that may require Gastrojejunostomy or Pyloroplasty typically experience:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe abdominal pain or discomfort after eating
- Bloating and early satiety
- Weight loss or malnutrition
- Recurrent gastric ulcers
- Food retention in the stomach
- Obstruction symptoms due to tumor or scarring
Procedure or Treatment
Gastrojejunostomy Procedure:
Performed either through open surgery or laparoscopically, this procedure involves:
General anesthesia is administered.
An incision is made in the abdomen.
The surgeon connects the lower part of the stomach to the jejunum, bypassing the duodenum.
The new connection allows food to move directly into the small intestine.
This surgery is often indicated in:
Gastric cancer with obstruction
Chronic pancreatitis
Peptic ulcer complications
Palliative care for unresectable tumors
Pyloroplasty Procedure:
Under anesthesia, the pylorus muscle is surgically cut and restructured to widen the outlet.
This allows stomach contents to pass more freely into the duodenum.
Often done alongside vagotomy (cutting of vagus nerve) to reduce acid secretion in ulcer patients.
Both procedures are followed by hospital observation, gradual reintroduction of food, and recovery monitoring to ensure normal digestion resumes.
Prevention and Management
While surgery is often a last resort, several steps can help manage or reduce the risk of conditions leading to obstruction:
- Timely treatment of ulcers and gastritis
- Avoiding NSAIDs and alcohol abuse
- Regular monitoring in patients with gastric cancer
- Managing chronic conditions like diabetes that can cause gastroparesis
- Early detection and management of digestive tumors
Benefits of Gastrojejunostomy / Pyloroplasty
- Restores normal digestion
- Relieves symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain
- Improves nutrition and weight gain
- Enhances quality of life in palliative care
- Allows for non-obstructed passage of food
- Reduces complications associated with chronic ulcers or gastric stasis
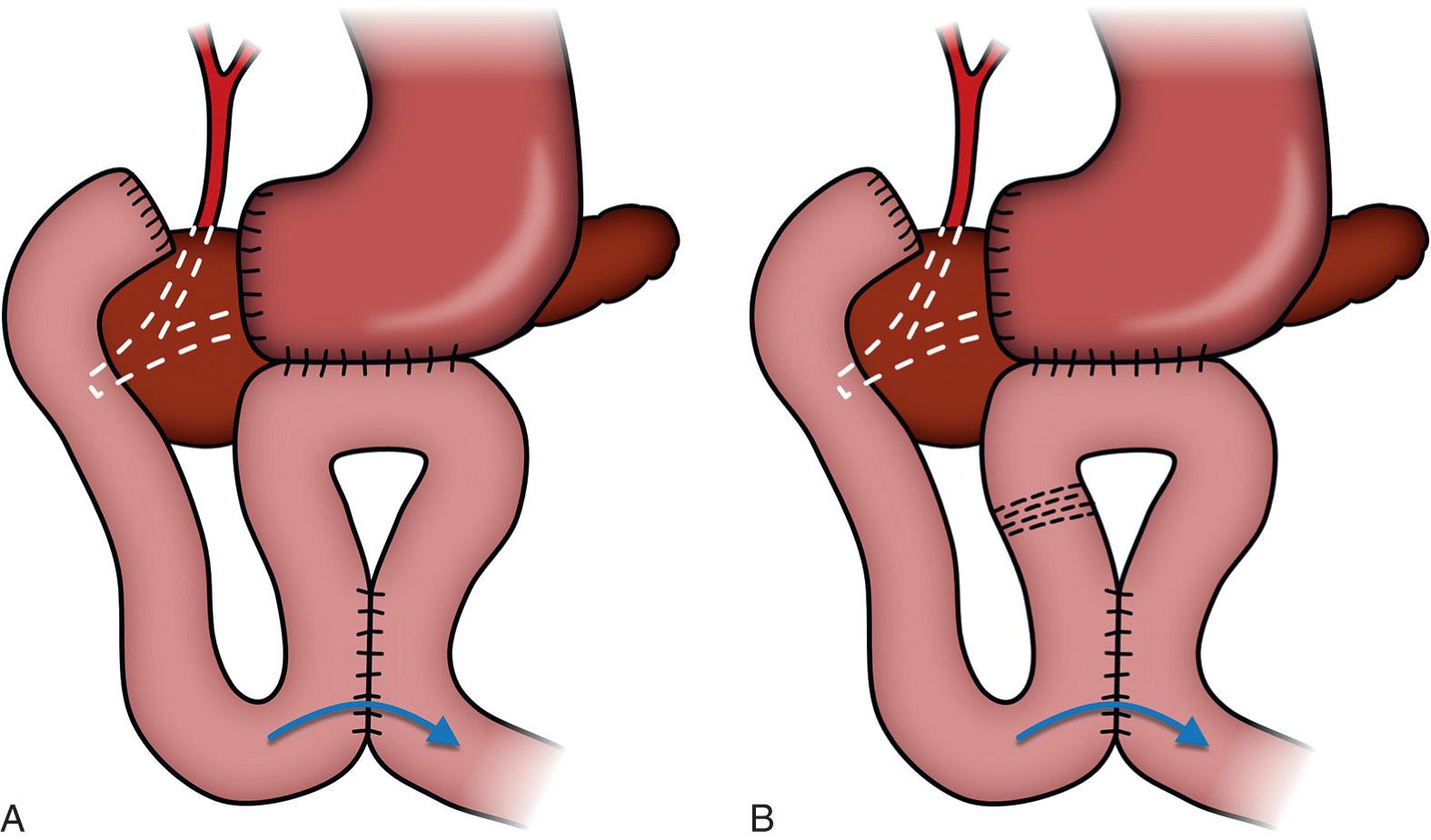
Types of Gastrojejunostomy
- Antecolic Gastrojejunostomy – Jejunum is brought in front of the colon.
- Retrocolic Gastrojejunostomy – Jejunum is passed behind the transverse colon.
- Roux-en-Y Gastrojejunostomy – A more complex reconstruction involving a long jejunal limb, often used in gastric bypass surgeries or cancer cases.
Types of Pyloroplasty
Heineke-Mikulicz Pyloroplasty – The most common method, involving a longitudinal cut and transverse closure of the pylorus.
Finney Pyloroplasty – A more extensive form used when a larger opening is needed.
Jaboulay Pyloroplasty – A side-to-side anastomosis between the stomach and duodenum, bypassing the pylorus without cutting it.
