What is Anal Polypectomy?
Symptoms of Anal Polyps
Many anal polyps do not cause noticeable symptoms and are often found incidentally. However, when symptoms occur, they may include:
- Rectal bleeding (bright red blood in stool)
- Mucus discharge from the anus
- Anal itching or irritation
- A feeling of incomplete bowel movement
- Unexplained changes in bowel habits
- Abdominal discomfort or cramps
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially rectal bleeding, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and care.
Procedure / Treatment: How is Anal Polypectomy Performed?
Anal polypectomy is typically a minimally invasive procedure and may be performed during a diagnostic endoscopy. The process generally includes:
Preparation:
Bowel cleansing with laxatives to ensure clear visibility.
Fasting for a few hours prior to the procedure.
Sedation or local anesthesia is usually administered.
Polyp Removal:
A flexible tube with a camera (colonoscope or sigmoidoscope) is inserted into the rectum.
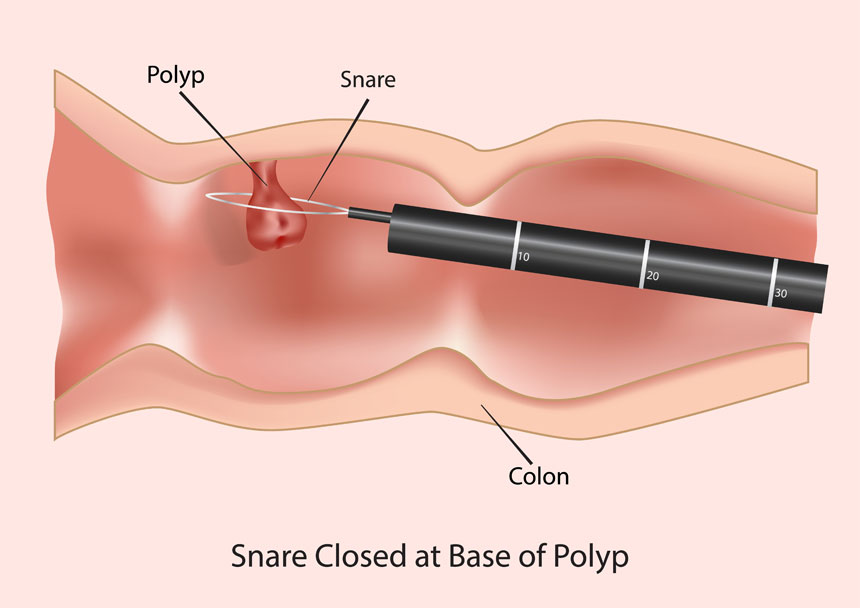
Special tools like forceps, snares, or electrocautery devices are used to grasp and remove the polyp.
Larger or suspicious polyps may be biopsied or sent for histopathological examination.
Recovery:
Most patients can return home the same day.
Mild discomfort, bloating, or minor rectal bleeding may occur temporarily.
Results of the biopsy, if taken, are usually available within a week.
Prevention of Anal Polyps
While it may not be possible to completely prevent polyps, certain lifestyle choices and screenings can significantly reduce the risk:
Regular screening: Especially after the age of 50 or earlier if you have a family history of polyps or colorectal cancer.
Dietary changes: High-fiber, low-fat diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Maintain healthy weight: Obesity is linked to a higher risk of polyps and colorectal cancer.
Avoid smoking and alcohol: These habits increase the likelihood of polyp formation.
Stay physically active: Regular exercise supports digestive health and overall wellness.
Benefits of Anal Polypectomy
- Cancer Prevention: Early removal of pre-cancerous polyps reduces the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Provides tissue samples for pathological examination.
- Symptom Relief: Reduces bleeding, discomfort, and changes in bowel habits.
- Minimally Invasive: Usually performed as an outpatient procedure with minimal recovery time.
- Cost-effective and safe: Quick and effective treatment for most polyps.
Types of Anal Polyps
Adenomatous Polyps (Adenomas):
Pre-cancerous growths with the potential to become malignant.
Most common type requiring removal.
Hyperplastic Polyps:
Usually small and non-cancerous.
Often found in the rectum and less concerning.
Inflammatory Polyps:
Common in people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Typically not precancerous.
Hamartomatous Polyps:
Typically benign and occur due to genetic conditions.
