What is Tuboplasty?
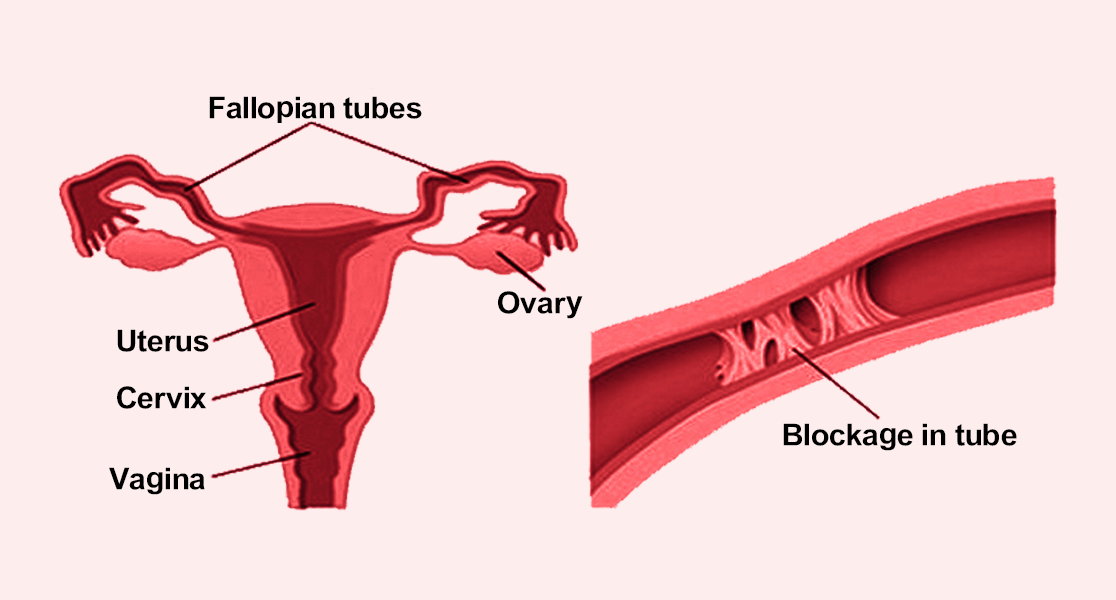
Symptoms of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Blocked fallopian tubes often do not show clear symptoms until a woman tries to conceive. However, possible signs include:
- Difficulty in getting pregnant (infertility)
- Pelvic pain, especially during menstruation or intercourse
- Painful periods
- Unusual vaginal discharge if infection is involved
- History of pelvic infections or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
Procedure / Treatment for Blocked Fallopian Tubes (Tuboplasty)
1. Diagnosis:
Before the surgery, tests like Hysterosalpingography (HSG), laparoscopy, or ultrasound are done to confirm blockages.
2. Surgical Process:
Tuboplasty is usually performed under general anesthesia using:
Laparoscopic Tuboplasty: Minimally invasive, using small incisions and a camera for precision.
Microsurgical Tuboplasty: Involves the use of a microscope for delicate repairs, especially when tubes are severely damaged.
The surgeon removes the blockage, separates adhesions, or reconstructs the tubes to restore patency (openness). In some cases, tubal reanastomosis (rejoining tubal segments) is done if the tube was previously tied for sterilisation.
3. Recovery:
Patients generally recover within a few days to weeks, depending on the surgical method used. Regular follow-ups are recommended to monitor healing and fertility outcomes.
Prevention of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
While not all cases are preventable, the following measures reduce the risk:
- Practicing safe sex to avoid STDs
- Timely treatment of pelvic infections
- Maintaining good reproductive health
- Early treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Avoiding multiple abortions or unmonitored intrauterine procedures
Benefits of Tuboplasty
- Restores natural fertility by reopening blocked tubes
- Avoids or delays the need for IVF in some cases
- Improves chances of natural conception
- Less invasive if done laparoscopically, leading to faster recovery
- Helps women with previous tubal ligation who desire pregnancy again
Types of Tuboplasty
Fimbrioplasty:
Repairs the fimbriae (finger-like ends) of the tubes if they are damaged or stuck together.Salpingostomy (Neosalpingostomy):
Creates a new opening in the tube if the end is blocked (commonly for hydrosalpinx).Tubal Reanastomosis:
Rejoins previously cut tubes, often after sterilisation reversal.Salpingolysis:
Removes adhesions around the tubes to free them.Cornual or Isthmic Tuboplasty:
Corrects blockages near the uterine end of the tube.
