What is Ovarian Cystectomy?
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Many ovarian cysts are asymptomatic, but when symptoms occur, they may include:
- Pelvic pain, especially during periods or intercourse
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder completely
- Menstrual irregularities
- Pain in the lower back or thighs
- Difficulty in conceiving (rare, but possible in some types of cysts)
Seek medical attention if there is sudden severe pain, fever, or vomiting, as it may indicate cyst rupture or ovarian torsion.
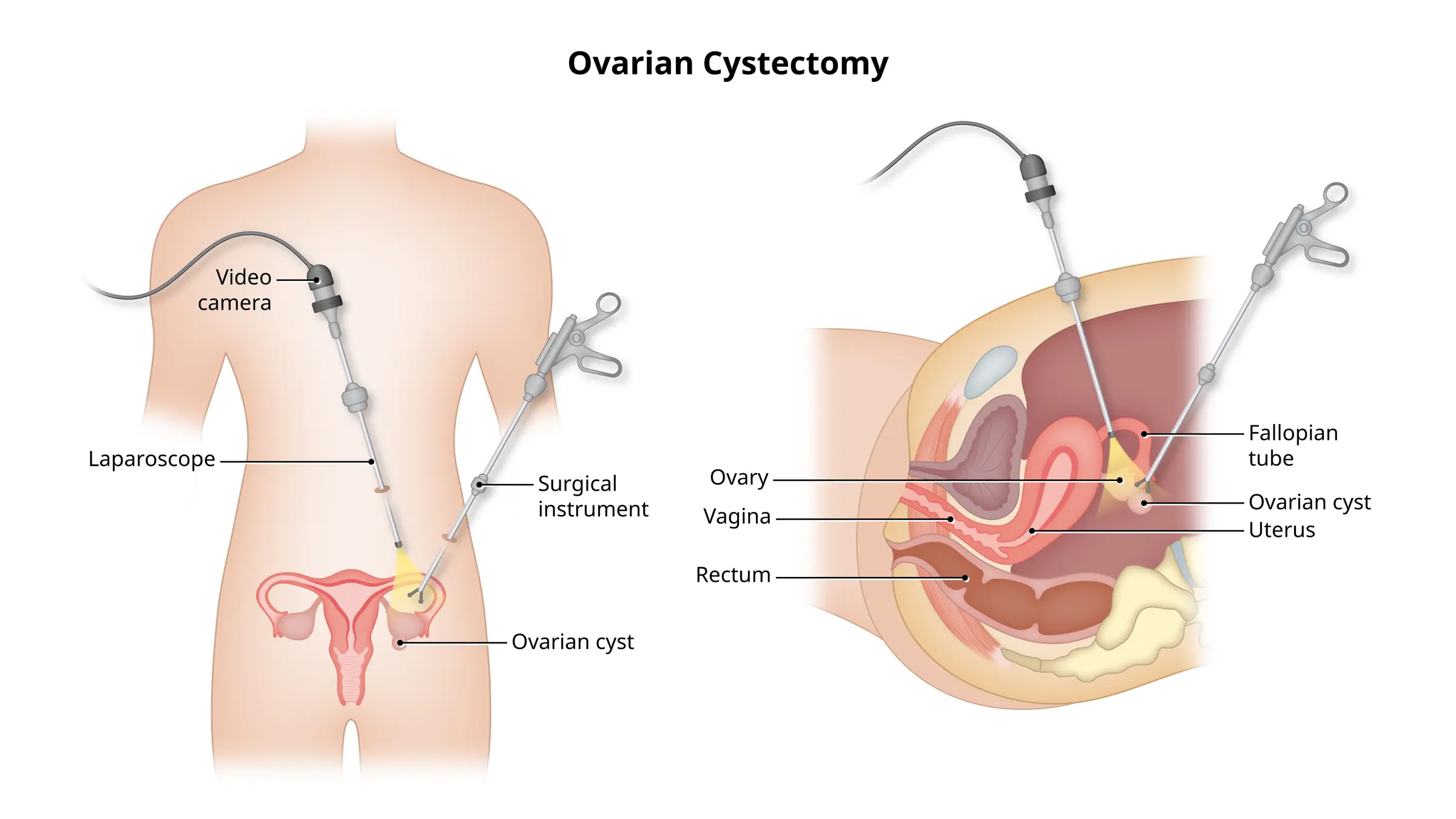
Procedure / Treatment
Preoperative Evaluation: Includes pelvic ultrasound, blood tests (including tumor markers if necessary), and clinical assessment.
Surgical Approach:
Laparoscopy (Keyhole surgery): Minimally invasive technique involving small incisions, a camera, and specialized instruments to remove the cyst. It offers faster recovery, less pain, and minimal scarring.
Laparotomy (Open surgery): Recommended for very large cysts or if malignancy is suspected. It involves a larger abdominal incision.
During Surgery: The cyst is carefully separated from the ovary and removed, preserving healthy ovarian tissue to maintain hormonal function and fertility.
Postoperative Care: Includes pain management, early mobilisation, and follow-up for histopathology results if the cyst is sent for analysis.
Prevention
While ovarian cysts cannot be completely prevented, the following can help:
Regular gynecological check-ups: Early detection and monitoring of cysts.
Hormonal contraceptives: May reduce the recurrence of functional cysts.
Managing underlying conditions: Like PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) through lifestyle modifications and medical treatment.
Awareness of symptoms: Prompt consultation for pelvic pain or menstrual irregularities.
Benefits of Ovarian Cystectomy
- Relief from pelvic pain and discomfort
- Preservation of ovarian function and hormonal balance
- Reduced risk of cyst rupture or torsion
- Accurate diagnosis through histopathological examination
- Enhanced fertility in cases where cysts were interfering with ovulation
Types of Ovarian Cysts Treated with Cystectomy
- Functional cysts: Such as follicular or corpus luteum cysts (though often resolve on their own)
- Dermoid cysts (Mature cystic teratomas)
- Endometriomas (Chocolate cysts)
- Cystadenomas (serous or mucinous)
- Hemorrhagic cysts
- Other benign cystic lesions
