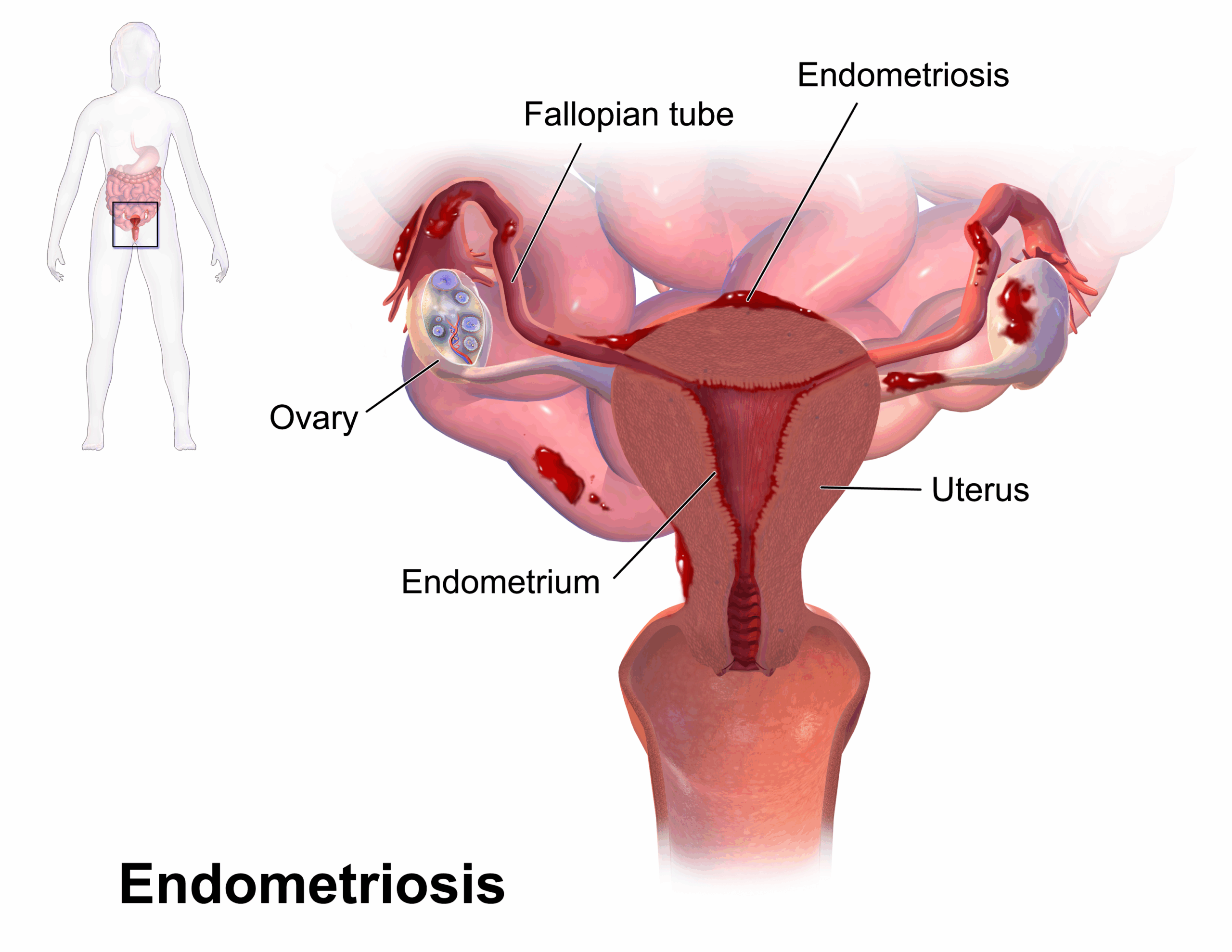
What is an Endometriotic Cyst?
Symptoms of Endometriotic Cyst
Endometriotic cysts may show no symptoms in some women, while others may experience:
- Pelvic pain, especially during menstruation (dysmenorrhea)
- Pain during intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Lower abdominal or pelvic discomfort outside menstrual periods
- Heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding
- Pain during urination or bowel movements, especially during periods
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
- Fatigue or general weakness
If you experience these symptoms, consult your gynecologist for timely evaluation.
Procedure or Treatment for Endometriotic Cyst
Treatment depends on the size of the cyst, severity of symptoms, and fertility plans:
Medical Management
Hormonal therapy such as birth control pills, GnRH agonists, or progestins to suppress endometriosis and reduce cyst growth.
Pain relief medications like NSAIDs for symptom management.
Surgical Treatment
Laparoscopic Cystectomy: Minimally invasive surgery to remove the cyst while preserving ovarian tissue, preferred for women desiring pregnancy.
Oophorectomy: Removal of the entire ovary if the cyst is large, recurrent, or there is suspicion of malignancy.
Hysterectomy with oophorectomy: For severe cases not responding to other treatments, especially if fertility is not a concern.
Prevention of Endometriotic Cyst
There is no definite way to prevent endometriotic cysts, but managing endometriosis early helps reduce risk.
- Hormonal therapies may prevent recurrence after surgical removal.
- Regular gynecological check-ups if you have endometriosis.
- Healthy lifestyle with stress management and balanced diet to reduce inflammation.
Benefits of Treatment
- Relief from chronic pelvic pain and discomfort
- Improved menstrual regularity
- Enhanced fertility outcomes in women planning pregnancy
- Better quality of life and daily functioning
- Reduced risk of complications, such as cyst rupture or damage to ovarian reserve
Types of Endometriotic Cysts
Endometriotic cysts are classified mainly based on location and nature:
Ovarian Endometriomas (Chocolate Cysts) – Most common type, found within ovaries, filled with old blood.
Superficial Endometriosis Lesions – Small implants on ovary surface, not forming a cyst but may co-exist with endometriomas.
Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis (DIE) – Though not cystic, severe form infiltrating pelvic organs, sometimes associated with endometriomas.
