What is Wound Debridement and Closure?
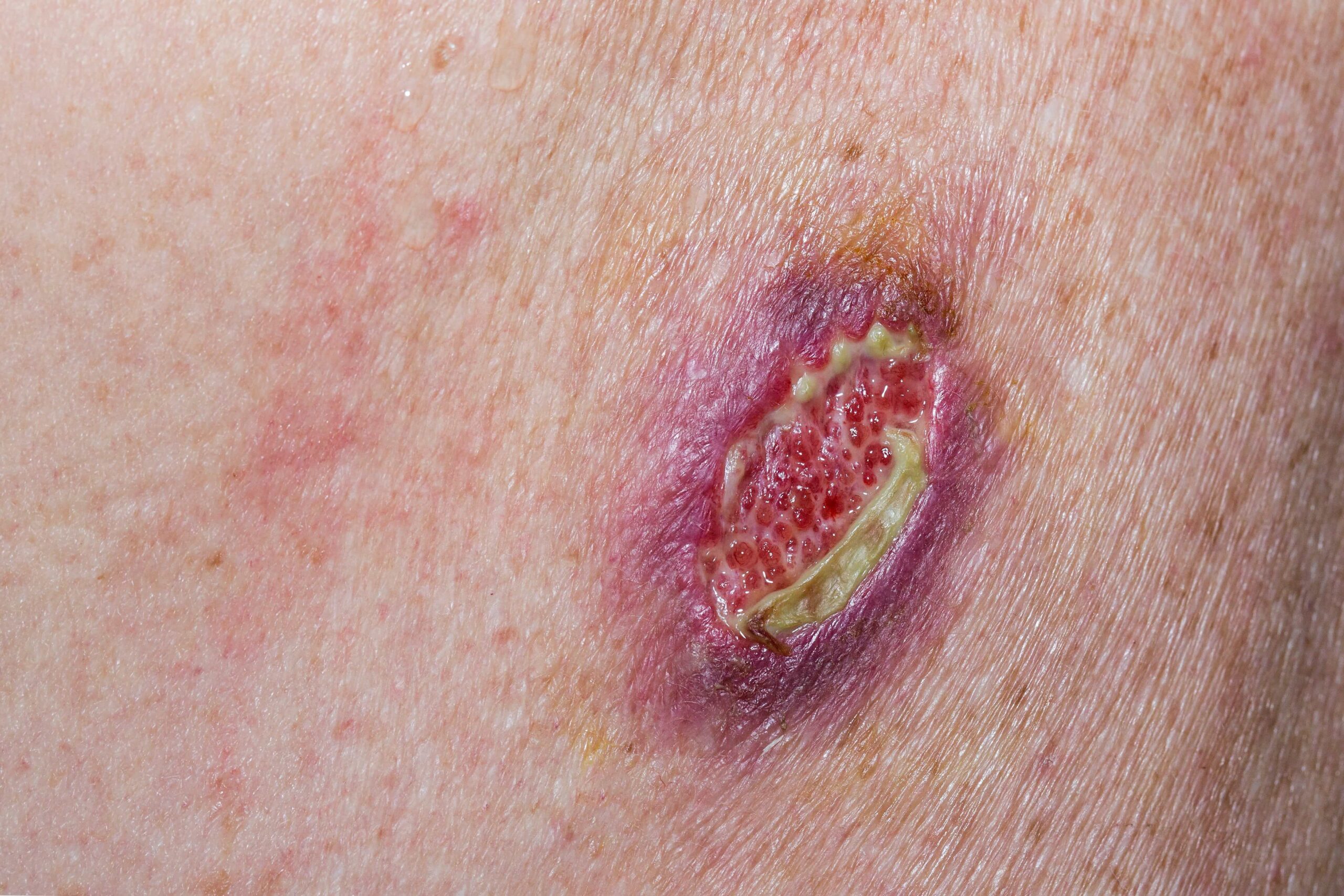
Common Symptoms That May Require Debridement and Closure
Patients with wounds that require this procedure may exhibit:
- Persistent pain at the wound site
- Swelling, redness, or warmth around the area
- Discharge or foul odor from the wound
- Delayed healing or open wound edges
- Signs of infection such as fever or pus formation
- Necrotic (black, dead) tissue visible in the wound
- Non-responsive wounds after conservative treatments
Procedure or Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. It may include:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Antifungal medications for yeast infections
- Hormonal creams for dryness or atrophy
- Lifestyle changes, proper hygiene, and probiotics
- Surgical correction for structural issues if needed
Types of Wound Debridement
There are several methods used depending on the wound’s condition, size, and the patient’s overall health:
Surgical Debridement
Performed in an operating room or clinic under anesthesia.
Dead or infected tissue is physically removed using surgical instruments.
Fastest and most effective method for large or deep wounds.
Mechanical Debridement
Uses techniques like wet-to-dry dressings or wound irrigation.
Tissue is removed along with dressings during dressing changes.
Autolytic Debridement
Utilizes the body’s own enzymes and moisture to liquefy dead tissue.
Achieved with moisture-retaining dressings.
Painless and suitable for less severe wounds.
Enzymatic Debridement
Application of topical agents containing proteolytic enzymes.
Helps break down necrotic tissue over time.
Used for patients who cannot undergo surgery.
Biological Debridement (Maggot Therapy)
Sterile maggots are applied to the wound to consume dead tissue.
Rarely used, but effective for certain chronic wounds.
Wound Closure Techniques
Once the wound is cleaned and free of infection, the next step is closure to ensure proper healing:
- Primary Closure (Sutures/Staples): Immediate closure of clean wounds.
- Secondary Closure: Wounds left open to heal naturally due to high infection risk.
- Delayed Primary Closure: Initially left open, then closed after a few days once infection risk is reduced.
- Skin Grafting or Flap Surgery: Used for large or deep wounds, especially where skin loss is significant.
Procedure or Treatment Overview
- Initial Assessment: Evaluation of wound depth, size, contamination, and infection.
- Cleaning: Irrigation with sterile solutions to remove debris and bacteria.
- Debridement: Selection and application of the most appropriate debridement method.
- Infection Control: Use of antibiotics if required.
- Closure: Depending on the wound, a suitable method of closure is applied.
- Dressing and Monitoring: Regular wound care, dressing changes, and follow-up.
Prevention of Complications
To prevent post-traumatic wound complications:
- Clean wounds promptly and thoroughly.
- Seek immediate medical attention for deep, dirty, or infected wounds.
- Maintain good hygiene and change dressings as advised.
- Control blood sugar levels if diabetic, as it affects wound healing.
- Avoid smoking, as it impairs circulation and delays healing.
Benefits of Timely Wound Debridement and Closure
- Promotes faster and more efficient healing
- Reduces the risk of serious infections like sepsis
- Minimizes scarring and preserves tissue integrity
- Prevents spread of infection to surrounding tissue
- Improves mobility and function in injured areas
- Enhances overall patient comfort and outcomes
Who Needs This Procedure?
- Accident victims with contaminated or large wounds
- Patients with burns, lacerations, or puncture wounds
- Individuals with diabetic ulcers or bedsores
- Patients with post-surgical wound complications
- Anyone with non-healing or infected wounds
