What is Scrotal Swelling?
Symptoms of Scrotal Swelling
The symptoms of scrotal swelling vary based on the underlying cause, but common signs include:
- Visible enlargement of the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort in the scrotum or groin area
- Redness or warmth in the scrotal skin
- A feeling of heaviness or dragging
- Presence of a lump or fluid-filled sac
- Fever and nausea (in cases of infection or torsion)
- Pain during urination or ejaculation
- Swelling extending to the penis or thighs (in severe cases)
Causes and Types of Scrotal Swelling
Scrotal swelling can result from various conditions, including:
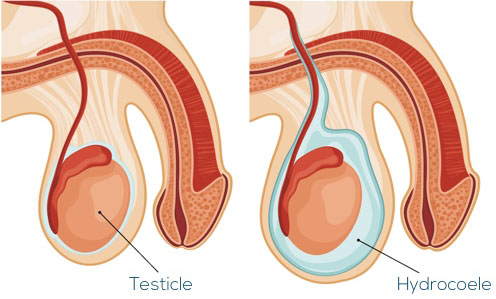
1. Hydrocele
A fluid-filled sac surrounding a testicle, common in newborns and older men. Usually painless.
2. Varicocele
An enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins, often affecting fertility.
3. Inguinal Hernia
Part of the intestine bulges into the scrotum through the groin, often seen as a soft swelling.
4. Epididymitis
Inflammation of the epididymis, often due to bacterial infection or sexually transmitted diseases.
5. Testicular Torsion
A medical emergency where the spermatic cord twists, cutting off blood supply to the testicle.
6. Orchitis
Inflammation of one or both testicles, often caused by viral infections like mumps.
7. Tumors or Testicular Cancer
Rare but serious; early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
Diagnosis and Investigations
A thorough clinical evaluation is essential. Diagnostic tools include:
- Physical examination
- Scrotal ultrasound – to evaluate fluid, masses, or blood flow
- Urine tests – to detect infections
- Blood tests – to check for signs of inflammation or cancer markers
- STD testing – if infection is suspected
- CT scan or MRI – in complex or unclear cases
Treatment & Management Options
Treatment depends on the cause of the swelling:
Medications
Antibiotics (for infections like epididymitis or orchitis)
Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs
Surgical Intervention
Hydrocelectomy (for hydrocele)
Varicocelectomy (for varicocele)
Hernia repair
Emergency surgery (for testicular torsion)
Tumor removal or orchiectomy (for testicular cancer)
Supportive Care
Scrotal elevation and cold compresses
Wearing supportive underwear
Rest and hydration
Prevention Tips
While not all types of scrotal swelling are preventable, these measures can help reduce risk:
- Practice safe sex to avoid STDs
- Avoid heavy lifting without support
- Regular self-examination of testicles
- Timely treatment of urinary or genital infections
- Stay vaccinated (e.g., against mumps)
Benefits of Early Detection and Treatment
- Prevents complications like infertility or permanent testicular damage
- Reduces pain and discomfort
- Promotes faster recovery
- Improves quality of life
- Enables better outcomes in case of cancer or torsion
