What is Anal Fissure?
An anal fissure is a small tear or cut in the lining of the anus, often caused by passing hard or large stools. It can lead to severe pain and bleeding during or after bowel movements. Though many fissures heal on their own or with conservative treatment, persistent or chronic fissures may require surgical intervention. One of the most effective surgical procedures is a lateral internal sphincterotomy.
Chronic anal fissures can be extremely painful and disruptive to daily life. Sphincterotomy offers a safe, reliable, and effective solution when conservative treatments fail. If you’re struggling with persistent fissure symptoms, consult a qualified colorectal surgeon to explore the benefits of this procedure and reclaim your comfort and well-being.
Symptoms of Anal Fissure
- Sharp pain during or after bowel movements
- Bright red blood on the toilet paper or stool
- Itching or irritation around the anus
- A visible crack or tear near the anus
- A small lump or skin tag near the fissure site in chronic cases
When is Surgery Needed?
Surgery is recommended when:
- The fissure becomes chronic (lasting more than 6–8 weeks)
- There is repeated recurrence despite medical management
- Severe pain and discomfort persist
- Other treatments like ointments, dietary changes, and sitz baths fail
Sphincterotomy: The Surgical Solution
What is Sphincterotomy?
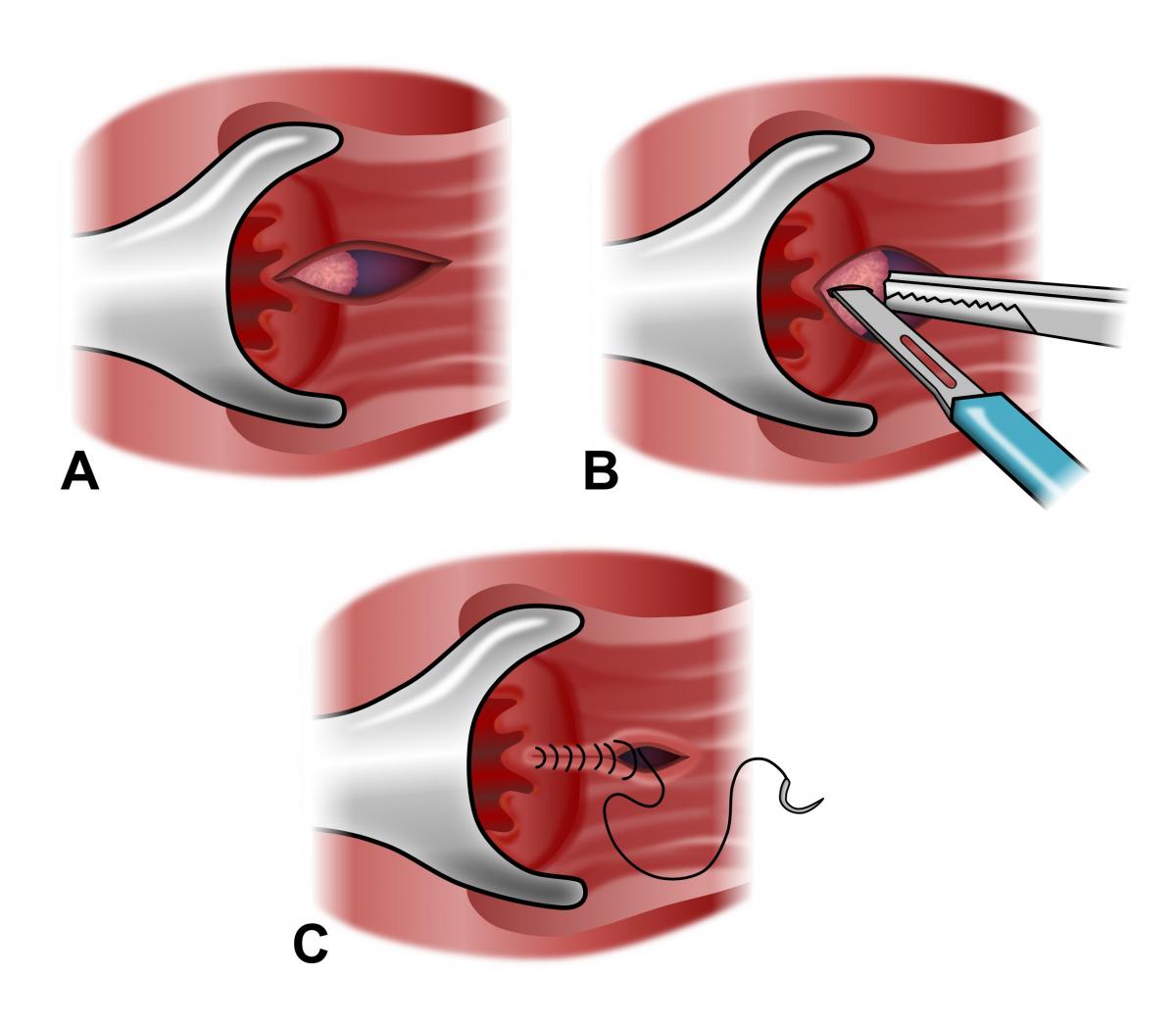
Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy is a minor surgical procedure that involves making a small incision in the internal anal sphincter muscle to reduce spasm, improve blood flow, and promote healing of the fissure. It is widely regarded as the gold standard treatment for chronic anal fissure.
Procedure Overview
- Pre-operative preparation: Fasting and possible bowel cleansing as advised by the doctor.
- Anesthesia: Usually performed under local, spinal, or general anesthesia.
- Surgical technique: A small incision is made in the internal anal sphincter muscle to relieve tension.
- Duration: The procedure typically takes 15–30 minutes.
- Post-operative care: Patients can usually return home the same day with instructions on hygiene, diet, and medications.
Benefits of Sphincterotomy
- High success rate (over 90%) in healing chronic fissures
- Quick pain relief and symptom improvement
- Minimal recovery time
- Reduced risk of recurrence
- Safe and effective with rare complications
Types of Fissure Treatments
Conservative Treatments (for acute fissures):
High-fiber diet and hydration
Stool softeners
Warm sitz baths
Topical ointments (nitroglycerin, calcium channel blockers)
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
Botox injection to relax the sphincter muscle
Surgical Treatment:
Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy (most common and effective for chronic fissures)
Prevention Tips for Anal Fissure
Eat a fiber-rich diet (fruits, vegetables, whole grains)
Drink plenty of water to avoid constipation
Avoid straining during bowel movements
Maintain good anal hygiene
Exercise regularly to support healthy digestion
Use stool softeners if needed, especially after surgery
