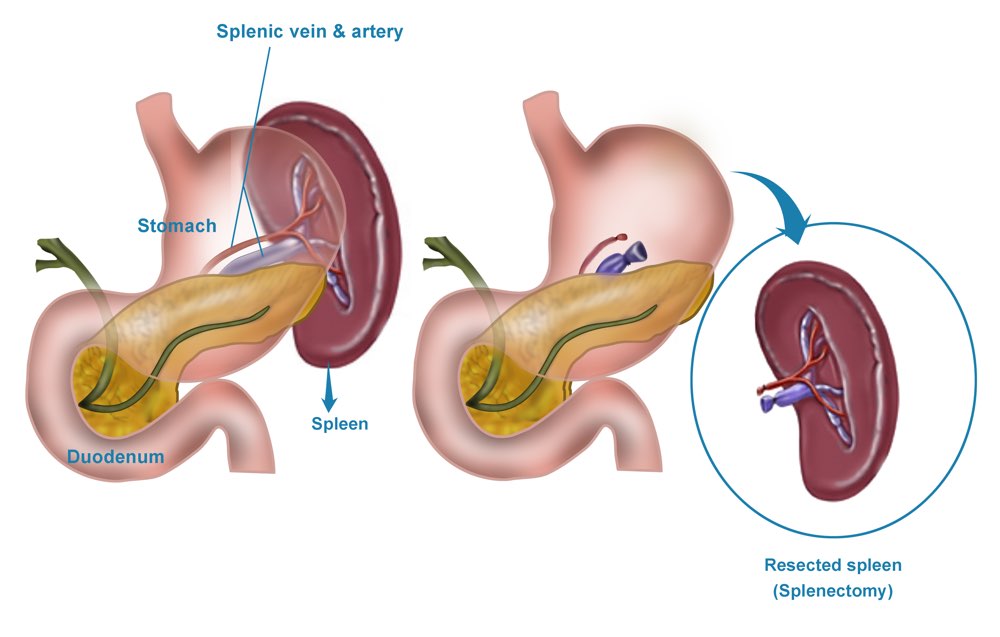
What is a Splenectomy?
A splenectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the spleen, an organ located in the upper left side of the abdomen, just beneath the rib cage. The spleen plays a crucial role in filtering the blood, fighting infections, and managing red and white blood cells. Splenectomy is often performed due to traumatic injury, rupture, or hematological disorders such as sickle cell disease, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), thalassemia, or lymphoma.
Depending on the condition, the splenectomy may be partial (removal of part of the spleen) or total (entire spleen removal).
Symptoms Indicating the Need for a Splenectom
Symptoms vary depending on the underlying cause but may include:
- Pain or tenderness in the upper left abdomen
- Frequent infections
- Easy bleeding or bruising
- Anemia and fatigue
- Enlarged spleen (splenomegaly)
- Low platelet or white blood cell count
- Internal bleeding due to trauma
Common Reasons for Splenectomy
Trauma: Accidents or blunt force injuries that rupture the spleen, causing internal bleeding.
Hematological Disorders: Conditions such as:
Hereditary spherocytosis
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Sickle cell anemia
ITP (Immune thrombocytopenic purpura)
Thalassemia
Lymphoma or leukemia affecting the spleen
Cysts or Tumors: Benign or malignant growths in the spleen
Hypersplenism: An overactive spleen destroying blood cells prematurely
Types of Splenectomy Procedures
Open Splenectomy
Traditional method involving a large incision in the abdomen.
Preferred in emergency cases like trauma.
Laparoscopic (Minimally Invasive) Splenectomy
Involves smaller incisions and use of a laparoscope.
Less pain, quicker recovery, and shorter hospital stay.
Typically used for non-traumatic conditions.
Partial Splenectomy
Only part of the spleen is removed.
Preserves some immune function, used in selected cases.
Procedure & Treatment
Preoperative Preparation:
Vaccinations (against pneumococcus, meningococcus, and H. influenzae)
Blood tests and imaging (ultrasound or CT scan)
Discussion of risks and post-surgery care
Surgical Procedure:
Performed under general anesthesia
Either laparoscopic or open method is used
The spleen is carefully separated and removed
Drain may be placed if necessary
Postoperative Care:
Hospital stay ranges from 1-5 days
Pain management and antibiotics
Gradual return to daily activities
Lifelong infection prevention strategies
Benefits of Splenectomy
- Relief from symptoms caused by an enlarged or malfunctioning spleen
- Reduced bleeding and bruising in platelet disorders
- Improved red blood cell survival in hemolytic anemia
- Enhanced quality of life in patients with chronic hematological disorders
- Life-saving in cases of spleen rupture
Risks & Preventive Measures After Splenectomy
Since the spleen plays a role in immune defense, patients without a spleen are at increased risk for infections, especially by encapsulated bacteria. Preventive measures include:
- Vaccinations (pre- and post-surgery)
- Antibiotic prophylaxis (especially in children or high-risk adults)
- Prompt treatment for fever or infections
- Medical alert identification for emergencies
