What is Pancreatitis Surgery?
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas that can become severe and life-threatening if not managed properly. In cases where there are complications like pancreatic necrosis (dead tissue) or pseudocysts (fluid-filled sacs), surgery becomes necessary. Two common surgical procedures for complicated pancreatitis are:
Necrosectomy – removal of dead or infected pancreatic tissue.
Pseudocyst Drainage – removal or internal drainage of fluid-filled cysts that may cause pain, infection, or digestive problems.
These procedures aim to control infection, relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and promote recovery.
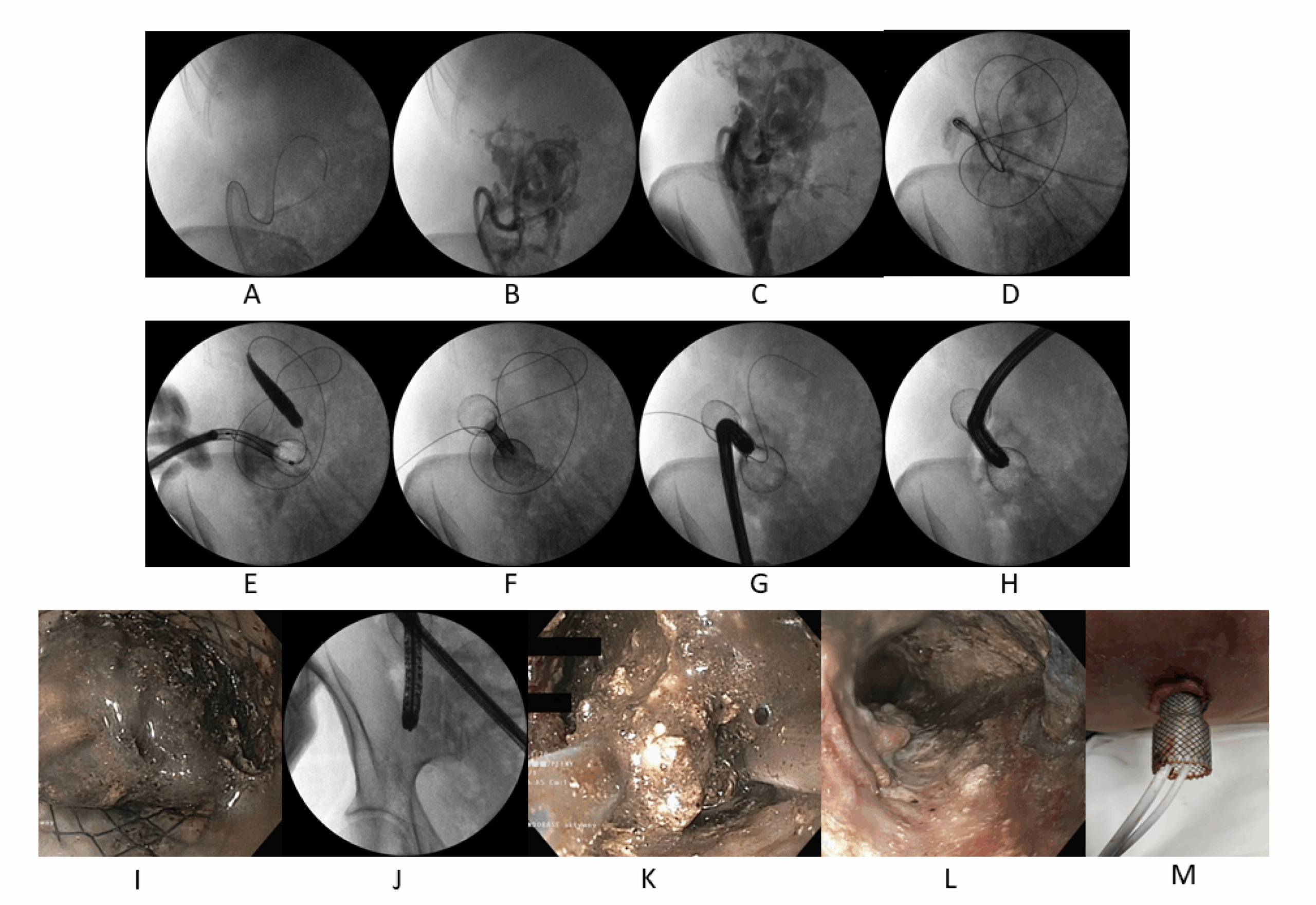
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Surgery
Patients with chronic or severe acute pancreatitis may experience:
- Severe and persistent abdominal pain
- Fever and signs of infection
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weight loss
- Jaundice
- Digestive difficulties
- Palpable abdominal mass
- Failure to respond to medication or endoscopic treatment
If complications like necrosis or pseudocyst formation are identified on imaging, surgical intervention is considered.
Surgical Procedures and Treatment Options
1. Necrosectomy
Necrosectomy is performed to remove dead or infected pancreatic tissue. The procedure can be done using:
Open Necrosectomy: Traditional surgical approach through an abdominal incision.
Minimally Invasive Surgery: Using laparoscopy or video-assisted retroperitoneal debridement (VARD) for reduced recovery time.
Endoscopic Necrosectomy: Performed using an endoscope via the stomach or intestines for selected patients.
2. Pseudocyst Drainage
Pseudocysts are drained when they become large, symptomatic, infected, or rupture-prone. Drainage techniques include:
Endoscopic Drainage: A minimally invasive technique using a stent through the gastrointestinal tract.
Percutaneous Drainage: A needle and catheter are inserted through the skin under imaging guidance.
Surgical Drainage: Involves internal drainage into the stomach or intestine (cystogastrostomy or cystojejunostomy).
Prevention of Pancreatitis and Its Complications
While surgery addresses complications, prevention of pancreatitis or its recurrence involves:
- Avoiding alcohol consumption
- Maintaining a low-fat diet
- Managing gallstones and cholesterol levels
- Treating underlying conditions like diabetes or autoimmune disorders
- Avoiding smoking
- Regular monitoring if chronic pancreatitis is diagnosed
Benefits of Surgical Management
- Eliminates infection and reduces risk of sepsis
- Relieves abdominal pain and discomfort
- Prevents rupture of pseudocysts or spread of necrosis
- Improves digestion and nutritional status
- Shortens hospital stays in severe cases
- Enhances long-term quality of life
Types of Pancreatitis Requiring Surgery
- Severe Acute Pancreatitis: Particularly with infected necrosis
- Chronic Pancreatitis: With complications like obstructed bile ducts, pain, or pancreatic duct issues
- Pancreatic Pseudocyst: Causing symptoms or complications
- Pancreatic Abscess: Requiring drainage or debridement
