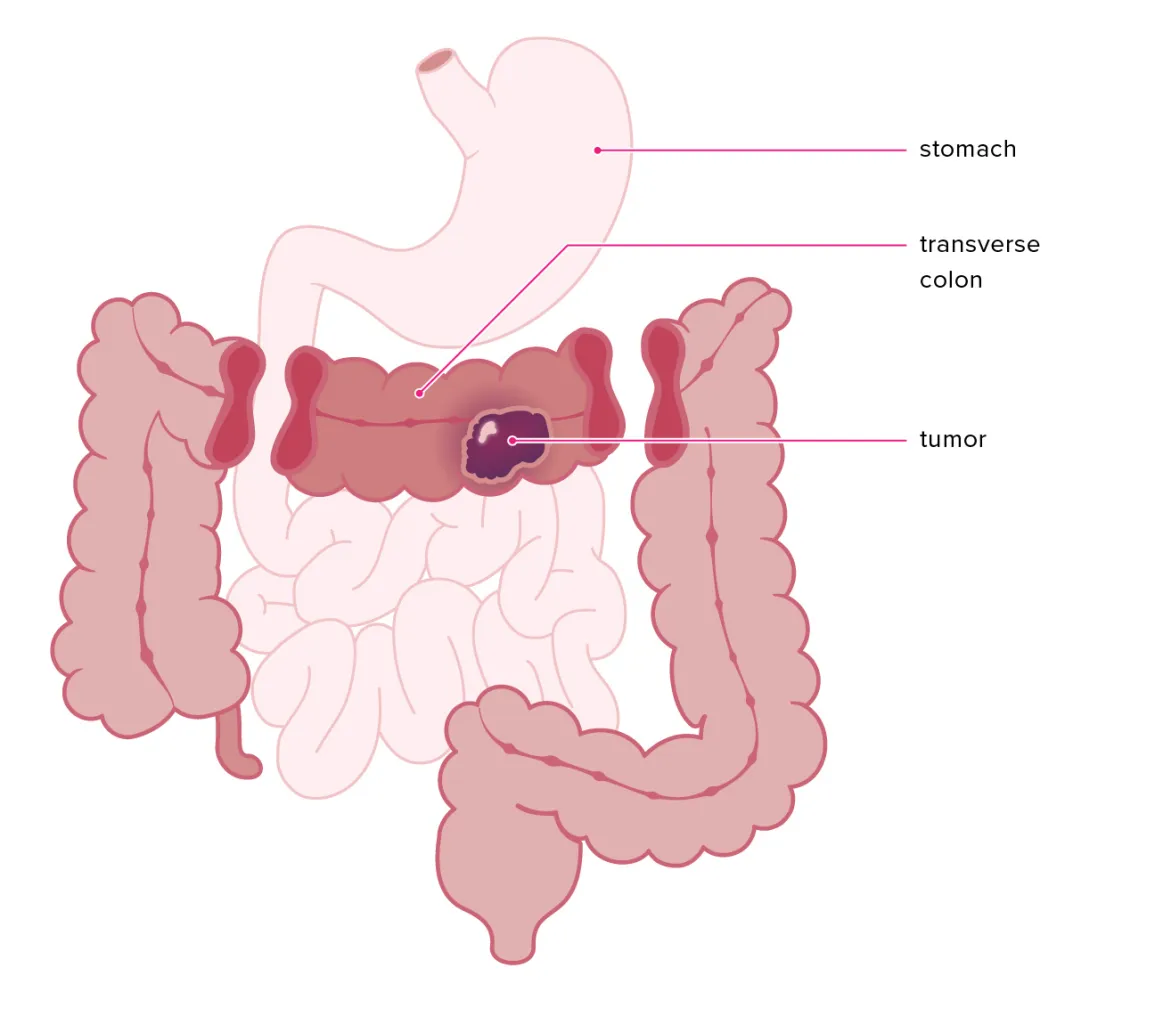
What is Bowel Resection & Anastomosis?
Symptoms That May Require Bowel Resection
Patients may experience one or more of the following symptoms, indicating a possible need for surgical evaluation:
- Chronic or severe abdominal pain
- Bowel obstruction or inability to pass stool or gas
- Persistent constipation or diarrhea
- Blood in the stool
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever or signs of infection
- Swelling or bloating of the abdomen
- Rectal bleeding
These symptoms are typically associated with underlying conditions like colon cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, or diverticulitis.
Procedure / Treatment
Preoperative Evaluation:
Before surgery, doctors perform imaging tests like CT scans, colonoscopy, or blood tests to assess the affected bowel segment.
Surgical Methods:
Open Surgery: Involves a larger incision in the abdomen to access and remove the damaged bowel.
Laparoscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive method using small incisions and a camera for guidance, offering quicker recovery and less postoperative pain.
Steps of the Procedure:
The affected bowel segment is carefully removed.
The two healthy ends of the bowel are joined together (anastomosis).
In some cases, a temporary or permanent colostomy or ileostomy may be created to divert waste.
Postoperative Care:
Hospital stay for a few days
Pain management and infection monitoring
Gradual return to normal diet
Follow-up imaging or endoscopy, if needed
Types of Bowel Resection & Anastomosis
- Small Bowel Resection – Removal of part of the small intestine (jejunum or ileum)
- Large Bowel (Colon) Resection – Also known as colectomy
- Right or Left Hemicolectomy – Removal of the right or left portion of the colon
- Sigmoid Resection – Removal of the sigmoid colon, often for diverticulitis
- Proctocolectomy – Removal of the rectum and colon, often for ulcerative colitis
- Ileocecal Resection – Removal of the junction between the small and large intestine
Prevention Tip
While not all bowel conditions can be prevented, the following measures can reduce your risk:
- Maintain a high-fiber, low-fat diet
- Stay hydrated and exercise regularly
- Undergo routine colonoscopy screenings after age 45 or earlier if at high risk
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake
- Manage chronic gastrointestinal diseases under medical supervision
- Address symptoms like rectal bleeding or severe constipation promptly
Benefits of Bowel Resection & Anastomosis
- Relief from chronic pain and discomfort
- Treatment or prevention of life-threatening complications like bowel perforation
- Improved quality of life and digestion
- Removal of cancerous or pre-cancerous tissue
- Restoration of normal bowel function
- Prevention of bowel obstruction or infections
