What is Laparoscopic Cystectomy?
Laparoscopic Cystectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove cysts from organs such as the ovaries, bladder, or kidneys. Unlike traditional open surgery, it involves making small incisions through which a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera and light) and surgical instruments are inserted, allowing the surgeon to view and remove the cyst precisely with minimal damage to surrounding tissues. It is commonly performed to treat ovarian cysts or bladder cysts that cause pain, complications, or are suspicious for malignancy.
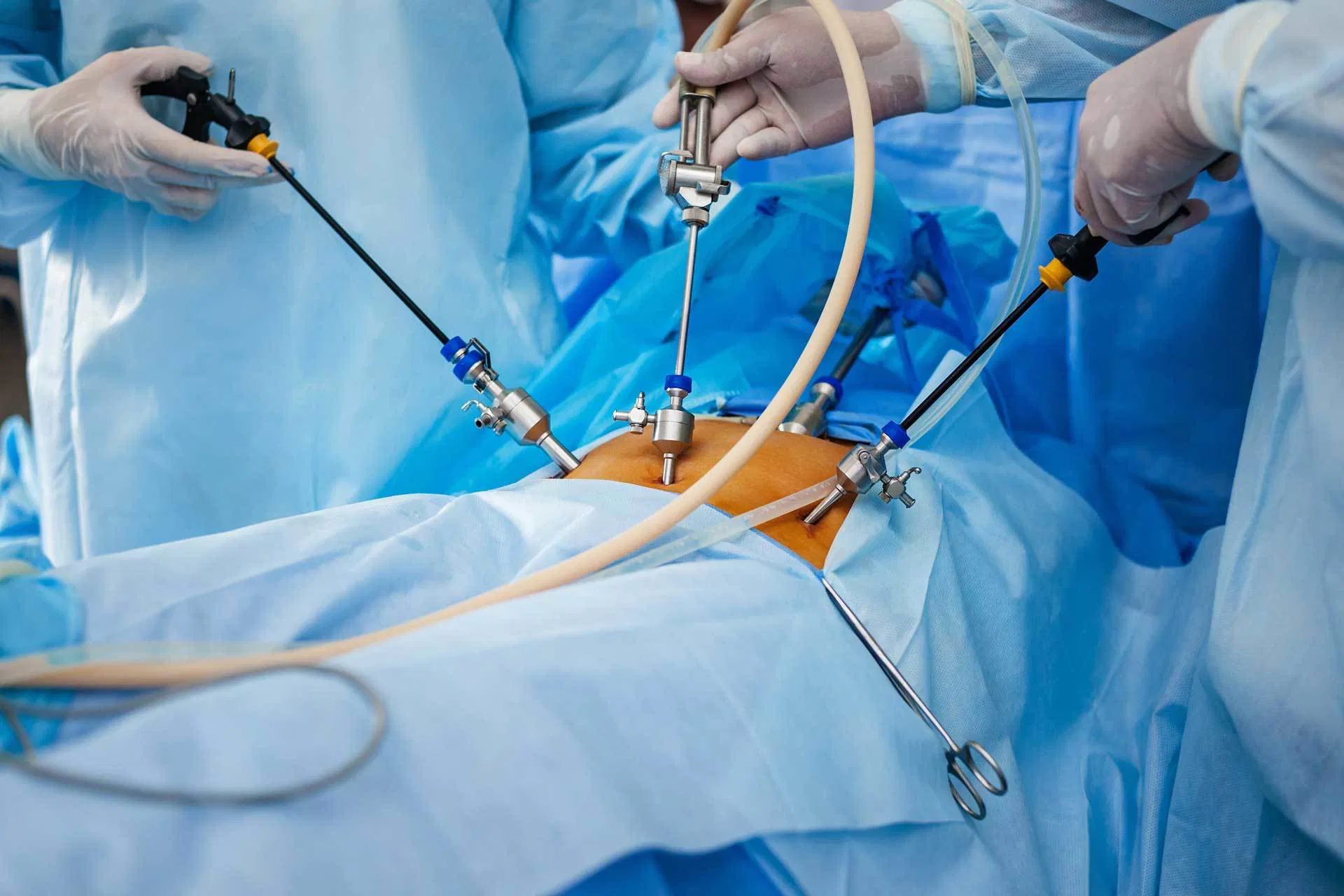
Laparoscopic cystectomy is a safe and effective surgical option for cyst removal with minimal complications and quicker recovery. If you are experiencing symptoms of abdominal or pelvic cysts, consult your doctor to assess if laparoscopic cystectomy is the right treatment for you.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Laparoscopic Cystectomy
Patients may require a laparoscopic cystectomy if they experience:
- Persistent abdominal or pelvic pain
- Bloating or abdominal swelling
- Painful urination or frequent urge to urinate (for bladder cysts)
- Pain during intercourse
- Irregular menstrual cycles or heavy bleeding (for ovarian cysts)
- Difficulty in emptying the bladder completely
- Back pain or pressure symptoms
Sometimes, cysts are found incidentally during scans without any symptoms but require removal if large, complex, or suspicious in nature.
Procedure / Treatment Details
Pre-operative preparation: Includes blood tests, ultrasound/MRI scans, and anesthesia assessment.
During surgery:
Small keyhole incisions are made in the abdomen.
The laparoscope is inserted to visualize the cyst.
Surgical instruments are used to separate and remove the cyst carefully while preserving the organ if possible.
Duration: Typically 1–3 hours depending on cyst size and complexity.
Post-operative care: Patients usually recover faster than open surgery, with minimal pain, smaller scars, and shorter hospital stay (often discharged within 1–2 days).
Prevention
While not all cysts are preventable, general preventive measures include:
- Regular pelvic or abdominal examinations for early detection
- Managing hormonal imbalances under medical guidance
- Maintaining a healthy weight and lifestyle
- Monitoring existing cysts through periodic ultrasounds
- Early treatment of urinary or gynecological infections to reduce complications
Benefits of Laparoscopic Cystectomy
- Minimally invasive with faster recovery
- Less postoperative pain and discomfort
- Reduced risk of infections and complications
- Smaller cosmetic scars
- Shorter hospital stay
- Early return to normal activities and work
Types of Laparoscopic Cystectomy
- Ovarian Laparoscopic Cystectomy: Removal of ovarian cysts while preserving ovarian tissue for fertility.
- Bladder Laparoscopic Cystectomy: Removal of cysts from the bladder wall.
- Renal Laparoscopic Cystectomy: For kidney cysts causing pain or affecting kidney function.
- Total Cystectomy (rare laparoscopic): Removal of the entire bladder, usually done for bladder cancer, though often performed via open or robotic approach.
