What is Cervical Stenosis?
Symptoms of Cervical Stenosis
Patients with cervical stenosis may experience:
- Neck pain and stiffness
- Numbness or tingling in arms, hands, or legs
- Weakness in limbs
- Difficulty with balance and coordination
- Problems with fine motor skills such as buttoning clothes
- In severe cases, loss of bladder or bowel control
Types of Surgical Procedures for Cervical Stenosis
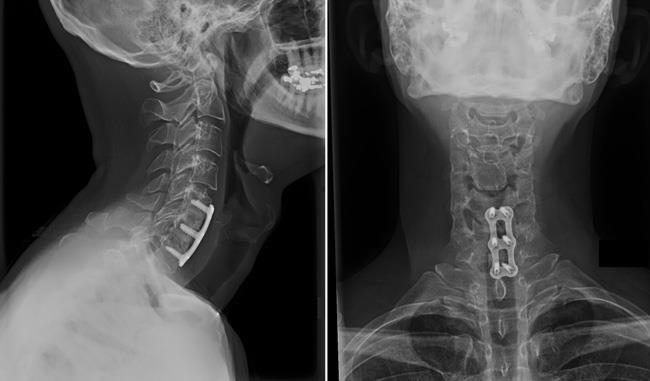
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF)
Removal of the problematic disc or bone spur from the front of the neck, followed by fusion to stabilise the spine.
Posterior Cervical Laminectomy
Removal of the lamina (back part of the vertebra) to widen the spinal canal and relieve pressure.
Cervical Laminoplasty
Reshaping and repositioning of the lamina to enlarge the spinal canal without removing the vertebra completely.
Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy
Removal of bone or tissue compressing a nerve root to relieve arm pain and nerve symptoms.
Procedure / Treatment
Surgery is recommended when conservative treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and injections fail to relieve symptoms, or if neurological deficits worsen. The surgical procedure depends on the extent and location of stenosis:
- Under general anaesthesia, an incision is made either in the front or back of the neck based on the chosen procedure.
- Compressed areas are decompressed by removing discs, bone spurs, or thickened ligaments.
- Fusion or reconstruction may be done to maintain spinal stability.
- Patients typically stay in the hospital for 1-3 days post-surgery and begin gradual rehabilitation for neck mobility and strength.
Prevention
While age-related stenosis cannot be entirely prevented, risk can be reduced by:
- Maintaining good neck posture
- Avoiding repetitive neck strain
- Regular exercise and neck strengthening
- Managing arthritis and bone health with a balanced diet and necessary supplements
Benefits of Surgery
- Relief from neck pain and stiffness
- Improved arm and hand strength
- Reduced numbness or tingling sensations
- Enhanced balance and walking ability
- Prevention of further neurological damage
- Improved quality of life and daily functioning
